Laboratory mills are unit operations designed to break solid materials into smaller particles. Laboratory mills use particle size reduction to homogenize or grind dry, wet, soft, hard, elastic, fibrous, and brittle materials. Read More…
As a world leader in industrial mixer manufacturing, KADY International offers high-performance industrial mixing machinery including top and bottom entry batch mixers, high shear mixers and chemical mixers.
Frain Industries is the world’s largest provider of high quality processing machinery! We offer a wide variety of mixers based on the product and volume our customers require.
The first Ross Three Roll Mill was built in 1869 and offered to paint & ink manufacturers. We revolutionized pigment dispersion — with superior consistency and finer dispersion than ever before. Today, the original Ross Three Roll Mills are still the standard by which all others are measured — in applications like magnetic coatings, cosmetics, paints, inks and high performance...
Admix, Inc. manufactures stainless steel mixing technologies & assists with tough mixing issues for a variety of markets. Choose from products such as basic mixers, Rotomaxx™ high torque mixers, BenchMix™ programmable lab mixers and more.
PerMix has been manufacturing mixing and blending equipment since 1954 for the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, cosmeceutical, food, and chemical industry. PerMix leads the industry in innovative, performance driven, Value Added Engineering mixing solutions of all types for all industries. With over 28 types of mixers, we lead the industry in mixing solutions when it comes to mixing powders,...
For more than 75 years, we have provided custom designed industrial mixing, drying, moving and controlling solutions for the food, plastics, minerals, chemicals, and biomass industries, manufactured to fit the specific requirements of one type of application- yours. It’s simple really, when you’re proud of your work, you sign your name to it. You’ll find it on everything we build. After...

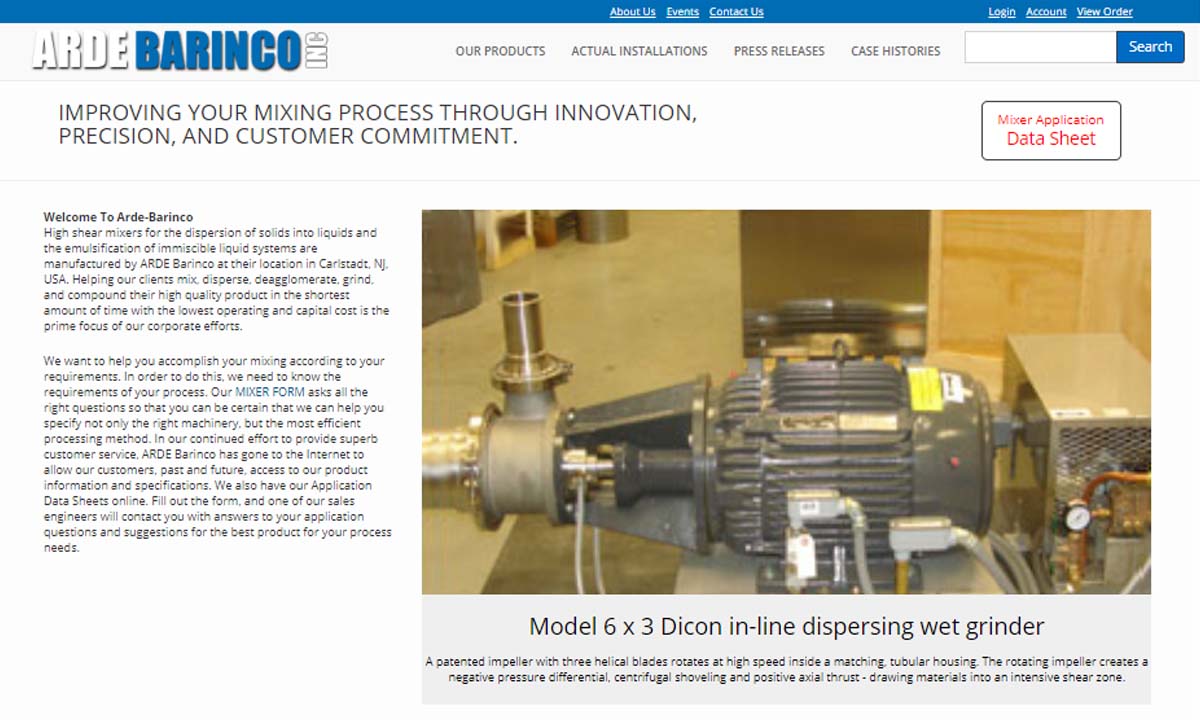
At ARDE Barinco, our goal is to help our clients mix, disperse, deagglomerate, grind and compound their high quality products in the shortest amount of time with the lowest operating and capital cost. Complete, up to date pricing for all standard mixers and spare parts is shown on our website.
More Laboratory Mill Manufacturers
What are Laboratory Mills?
Laboratory mills are utilized in a wide range of scientific areas, including food analysis, life science, materials testing, chemistry, and pharmaceuticals.
Hammer, disk, planetary ball, mortar, cutting mills, and rotor are available for achieving coarse, mid-range, and fine results, all the way down to the Nano range, less than 0.1μm.
There are also types of laboratory mills called freezer mills or cryogenic mills that freeze a material before reducing its particle size.

How Laboratory Mills Work
Laboratory mills utilize the mechanically generated force for pulverizing non-homogenous batch samples into smaller, homogenous, representative samples for quality control and analytical testing.
Their components include a grinding element like a cutting blade or beater housed within a disposable plastic or stainless steel milling chamber. Connection is made from the grinding element to a high-speed motor regulated by a digital controller or timer.
Considerations When Choosing a Laboratory Mill
When opting for a laboratory mill, speed, power, and cleanability are important parameters that must be considered. However, it is also important to bear in mind the equipment's throughput, yield, reproducibility, and, if necessary, the option of a cooling system.
Types of Laboratory Mills
The types of laboratory mills include:
Hammer Mills
These lab mills utilize a high-speed rotating steel hammer to grind the particles, and they have a sieve in the periphery that serves as a passage for the outflow of the sample from the grinding chamber.
Through the selection of various sieves, the distribution of the particle size in the sample can be varied. The hammer mill is typically used to produce a homogenous and fine sample.
The hammer mill can grind up to 300-gram samples, which is the amount requested for the falling number test.
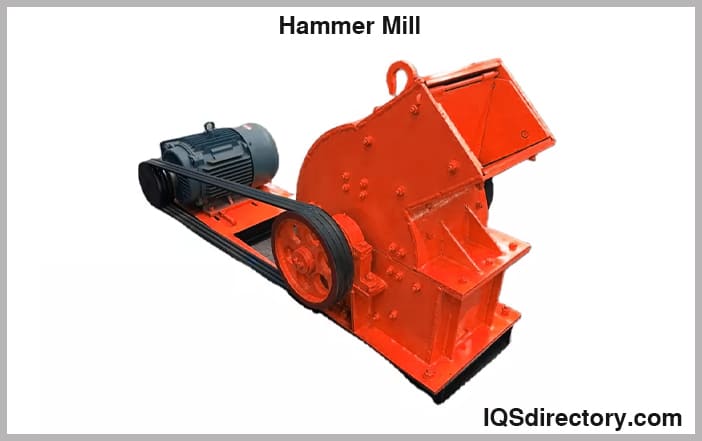

Because of the heat developed in the grinding operation and the high airflow through the grinding chamber, the hammer mill is unsuitable for determining grain moisture.
Disc Mills
This type of mill utilizes one rotating and one stationary metal disc with teeth for grinding the sample. Its main application is the determination of grain moisture due to its ability to grind grain without the loss of moisture.
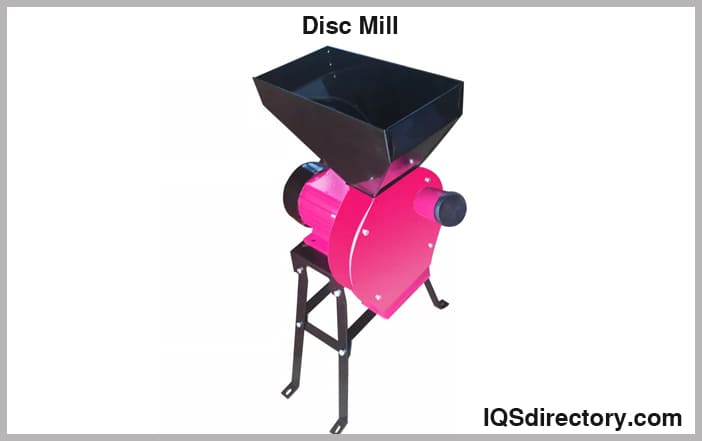

Varying the particle size from the mill can be done by adjusting the distance between the rotating and the stationary disc. There are also various types of discs to select.
Mortar Grinder Mill
A mortar grinder mill is a powerful grinder laboratory mill capable of ensuring homogenous sample preparation.
Samples can be added through two Plexiglas windows. The unit can be operated via an on/off switch, or it can be done through its built-in digital timer, with longer times giving results of finer particles.
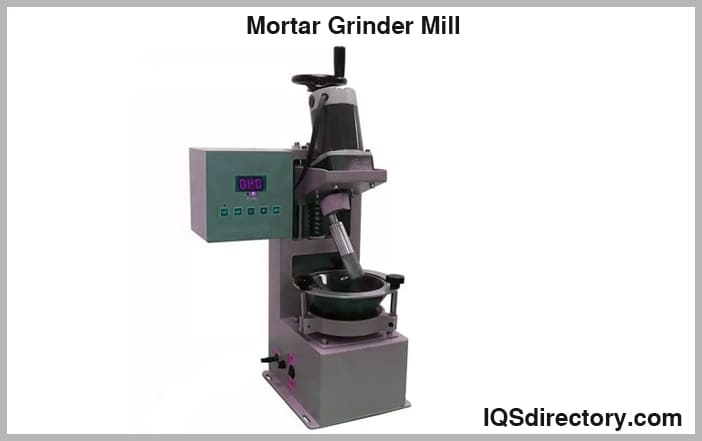

There are five grinding sets to select from, which must be harder than the sample: corundum, porcelain, chrome steel, agate, and stainless steel.
Furthermore, this type of lab mill consists of a safety switch and an overload switch to ensure safe and accurate operation. The pestle, mortar, and scraper can be easily cleaned, minimizing sample-to-sample contamination.
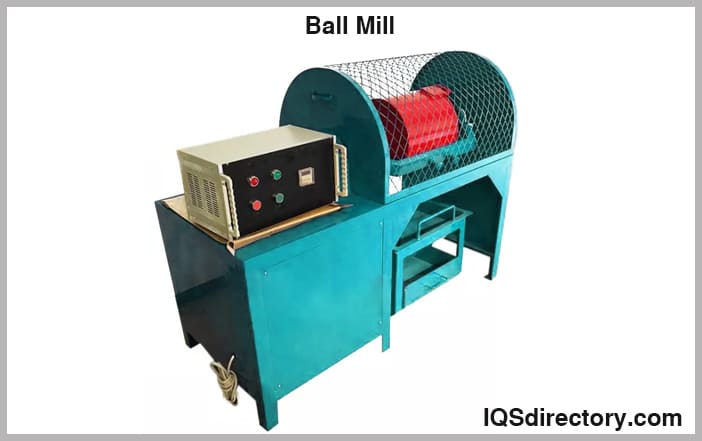
Ball Mill
This lab mill is an affordable mill that can be utilized in the preparation of samples with minimal loss. The unit's design offers quiet performance and reduced vibration, which in turn increases the comfort of the user and safety.

Applications and Benefits of Laboratory Mills
The applications and benefits of laboratory mills include:
Applications of Laboratory Mills
Laboratory Mills are mostly used in the following fields:
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Microbiology
- Pharmacology
- Physics
- Zoology
- Agronomy
- Medical science
- Pharmacy
Benefits of Laboratory Mills
- They provide high sample homogeneity – they improve the repeatability as well as the accuracy of analytical results
- They have a robust design-they exhibit excellent durability as well as a low cost of ownership
- They are suitable for oilseeds, grains, and more. They are flexible for grinding many different types of samples.
Choosing the Correct Laboratory Mills Supplier
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing Laboratory Mills from a Laboratory Mills Supplier, it is important to compare at least 5 or 6 Companies using our list of Laboratory Mills suppliers. Each Laboratory Mills Company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Laboratory Mills business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Laboratory Mills companies with the same message.





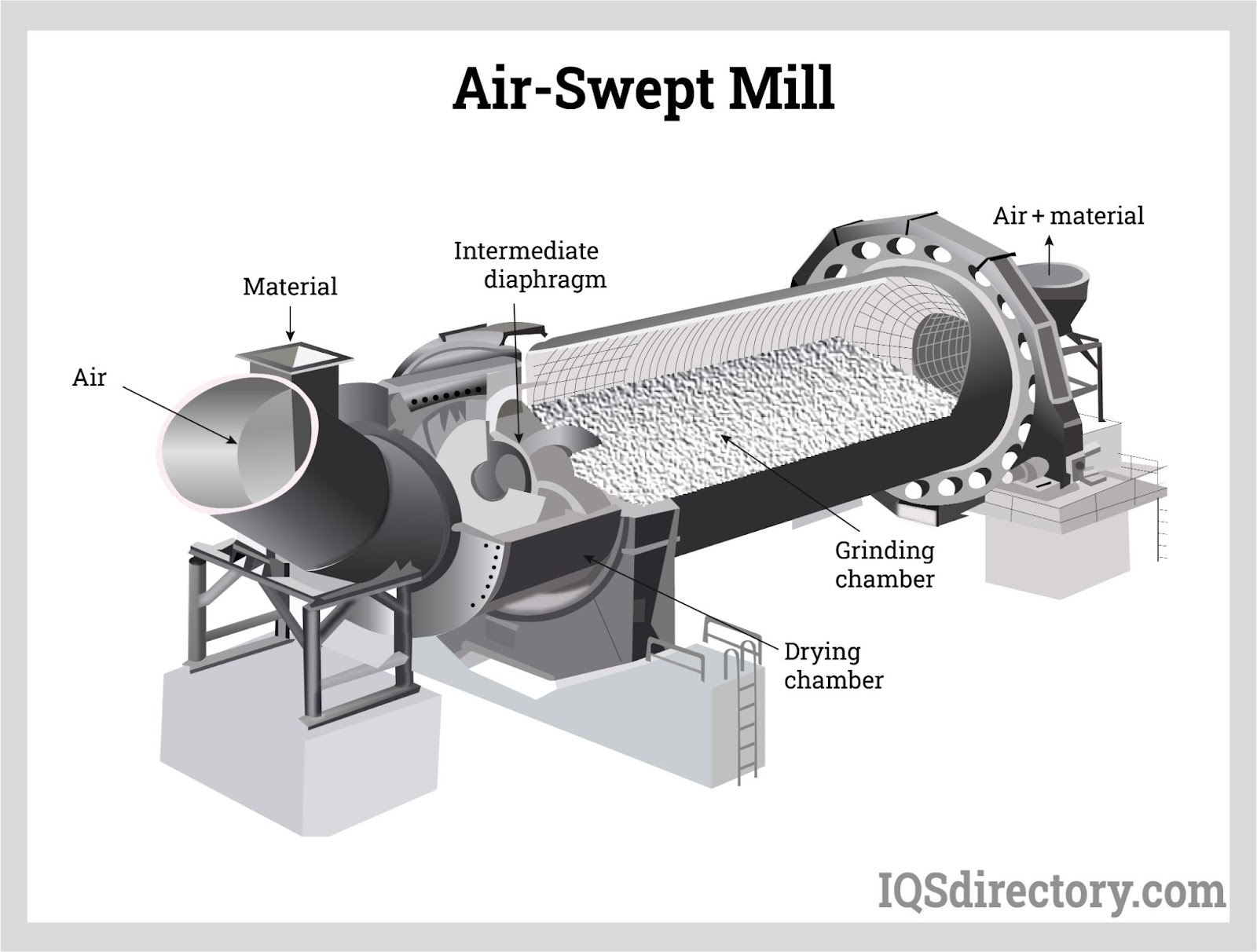




 Electric Heaters
Electric Heaters Industrial Dryers
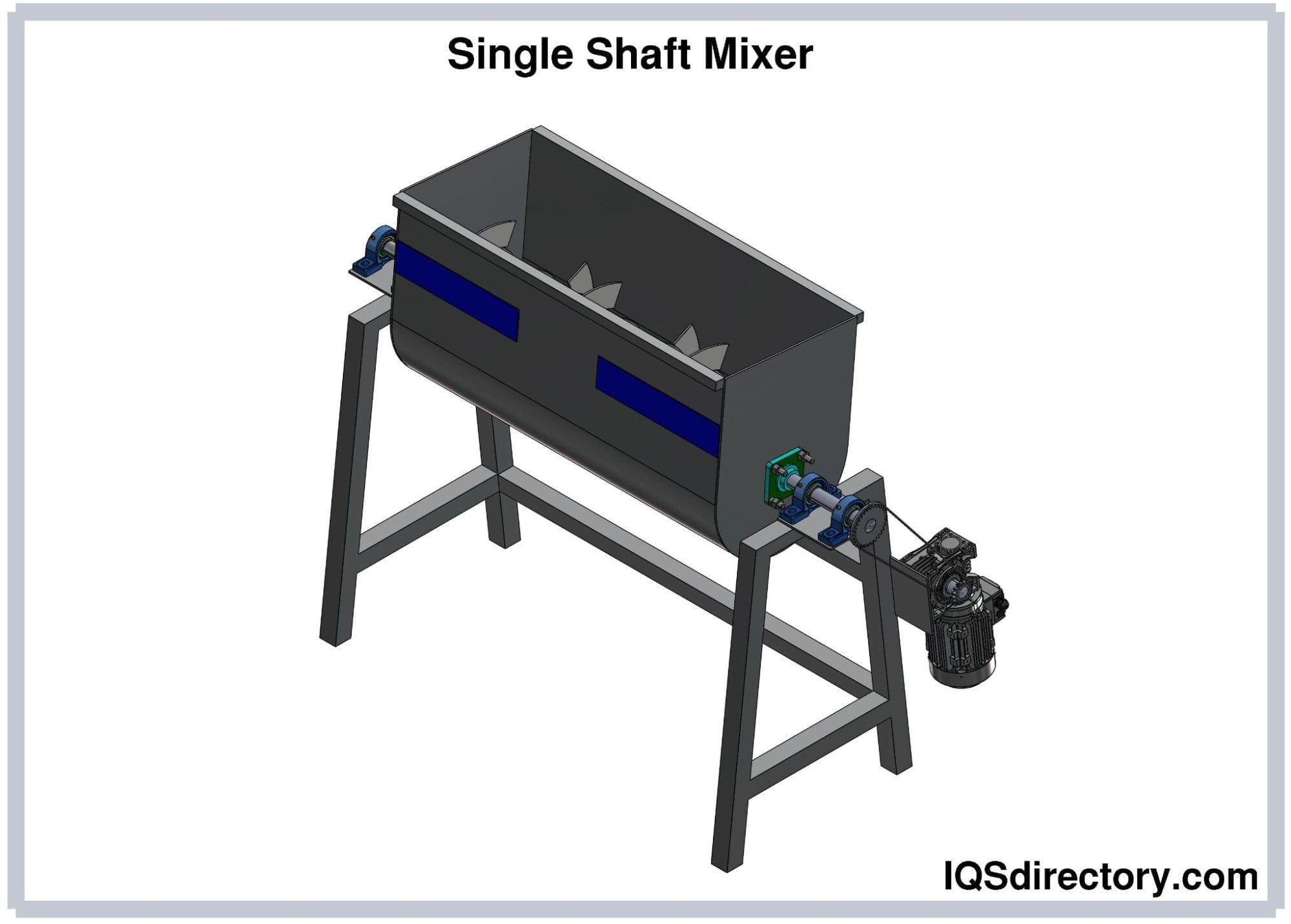
Industrial Dryers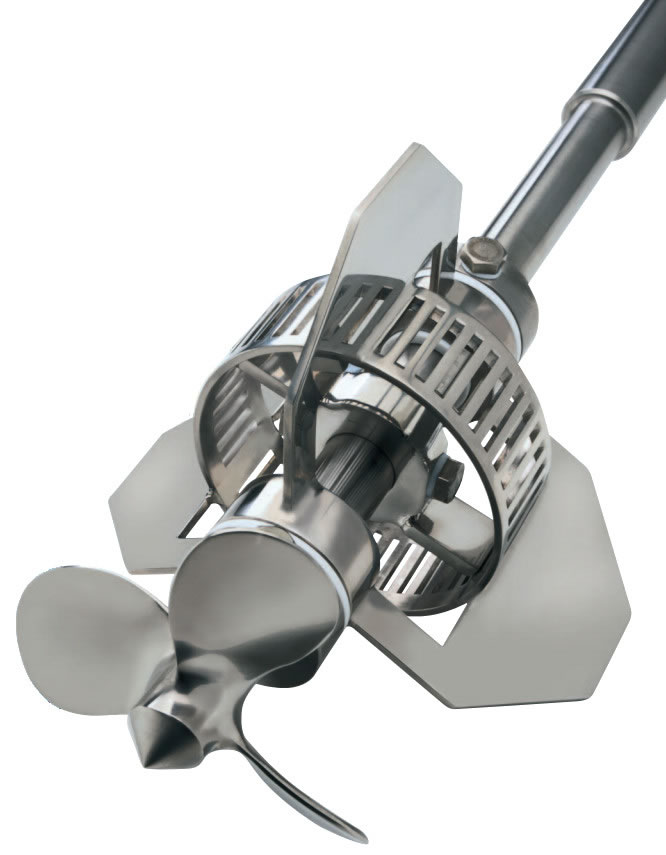 Industrial Mixers
Industrial Mixers Industrial Ovens
Industrial Ovens Pressure Vessels
Pressure Vessels Pulverizers
Pulverizers Vibratory Feeders
Vibratory Feeders Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services